In New Zealand, gas heaters are a popular choice for home heating. The two types of gas heaters; flued and unflued, differ mainly in their venting systems.
In this article we will explain the differenced between these gas heaters, covering their unique features, benefits and drawbacks.
Whether you are considering a gas fireplace or a portable heater, understanding the differences between flued and unflued options is crucial for making an informed decision.
What Is the Difference Between Flued and Unflued Gas Heaters?
In terms of operational differences, a substantial distinction between flued and unflued gas heaters lies in their respective methods of venting exhaust gases.
Flued heaters are typically designed with a flue or chimney, which directs the combustion by-products outside, ensuring a clean and healthy indoor environment. Conversely, unflued heaters expel these gases directly into the room where the heater is installed.
To better understand the differences, let’s consider the following aspects:
- Installation: Flued heaters require a more complex installation process involving the construction of a flue or chimney, which can add to the overall cost. Unflued heaters, however, are easier and less expensive to install.
- Efficiency: Unflued heaters generally provide rapid heat and are more efficient due to their direct release of heat into the room. Flued heaters, on the other hand, are less efficient as some heat is lost through the flue.
- Safety: Flued heaters are considered safer as they vent harmful gases outdoors, reducing the risk of indoor air pollution. Unflued heaters require adequate ventilation to ensure safety and have raised safety concerns in New Zealand.
- Flexibility: Unflued heaters offer greater flexibility as they can be easily moved from one room to another, unlike flued heaters which are fixed installations.
Flued Gas Heaters
What Are Flued Gas Heaters
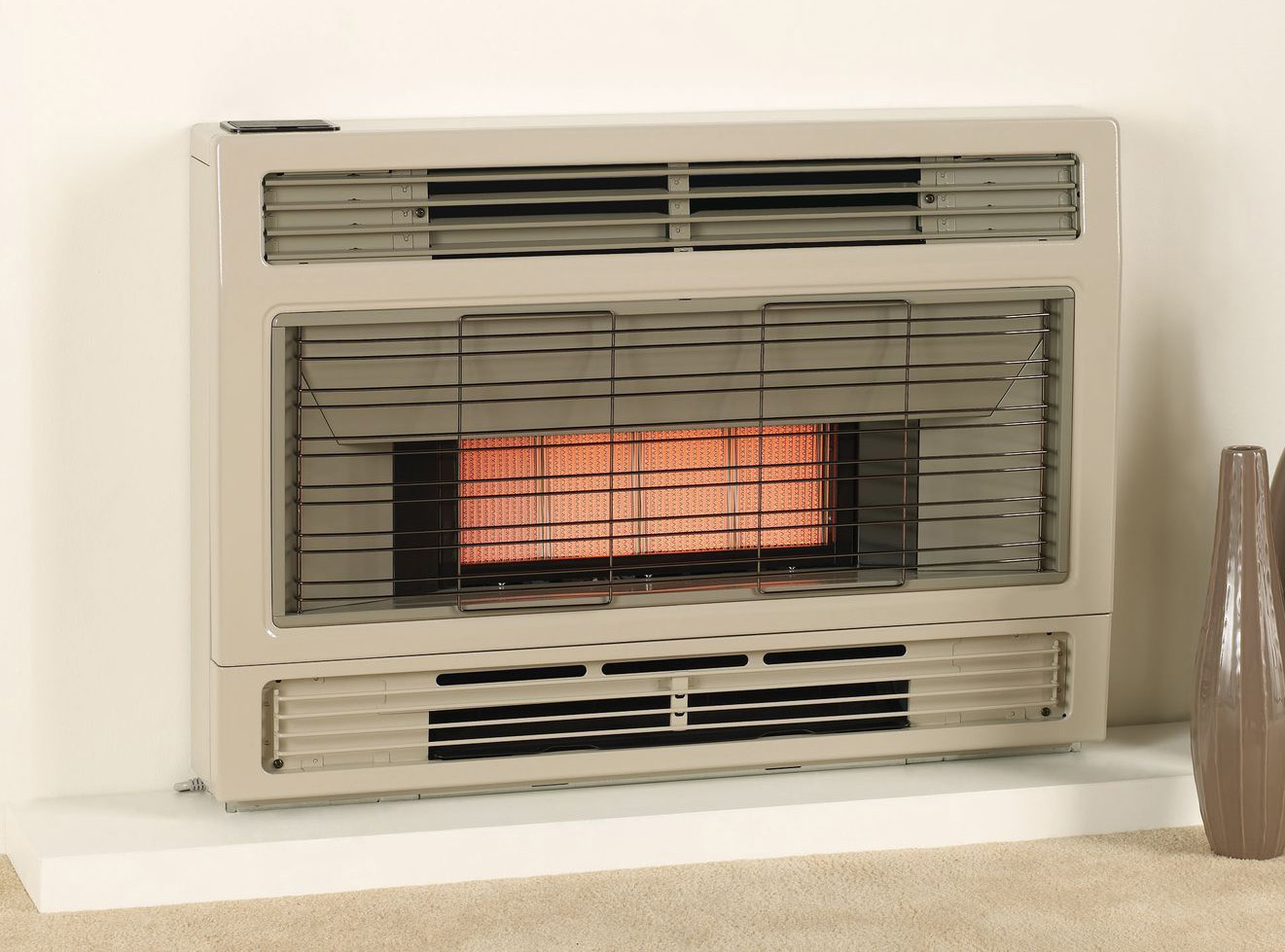

Flued gas heaters are heating systems that have flues or ducts, which safely expel combustion gases outside the premises. These heaters ensure that the indoor air quality remains unaffected by the by-products of the combustion process.
Features of Flued Gas Heaters
Flued gas heaters are renowned for their energy efficiency, which is a result of their design that allows heat to be evenly distributed throughout the room. They also feature a flue system, which removes combustion gases to the outside, making them a safer choice for indoor environments.
Furthermore, these heaters are versatile and can be installed in various locations while offering a range of heat output options. A noteworthy feature is their programmable thermostats, providing users with control over heating levels and energy consumption.
Lastly, flued gas heaters are designed to function optimally in adverse weather conditions, offering reliable and consistent heating solutions.
Pros of Flued Gas Heaters
The advantages of flued gas heaters extend beyond their distinctive features, offering a plethora of benefits to homeowners in New Zealand.
- Improved air quality: Unlike unflued heaters, flued heaters direct harmful emissions outside, resulting in a healthier indoor environment.
- Energy efficiency: Flued gas heaters are designed to provide consistent and efficient heat, proving to be cost-effective over time.
- Long-term solution: Owing to their robust construction and reliable performance, these heaters offer a durable heating solution that can withstand the test of time.
- Design flexibility: The versatility in installation locations, from wall-mounted to freestanding, allows homeowners to choose a heating solution that best fits their decor and space requirements.
Cons of Flued Gas Heaters
While appreciating the advantages of flued gas heaters, it’s important to also consider potential drawbacks that might influence a homeowner’s decision.
One of the main disadvantages is the initial cost; flued heaters can be more expensive to purchase and install than their unflued counterparts. They also require a dedicated flue or chimney, which can add to the complexity and cost of installation.
Furthermore, flued heaters can be less energy efficient than unflued units as some heat is lost through the flue.
Finally, these heaters require more maintenance and servicing to ensure the flue is clear and functioning properly.
However, despite these potential cons, they are still the recommended choice for gas heating in New Zealand.
Unflued Gas Heaters
What Are Unflued Gas Heaters
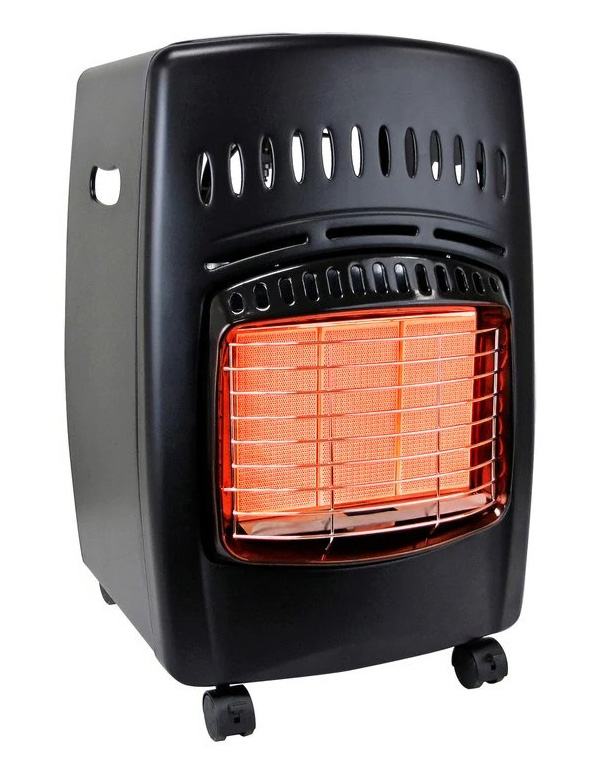

Unflued gas heaters, also known as ventless heaters, are heating systems that lack a flue or vent to direct combustion byproducts outside. They rely on indoor air for combustion and release the byproducts, typically water vapour and carbon dioxide, back into the room.
This design allows for high heat efficiency as no energy is lost through a vent. However, it necessitates proper room ventilation to avoid the build-up of harmful gases.
Unflued heaters are popular for their portability, ease of installation, and the ability to provide instant heat, making them suitable for supplemental or spot heating requirements.
Safety Concerns Relating to Unflued Gas Heaters
Unflued gas heaters can pose several safety and health concerns, particularly in enclosed spaces like homes. In New Zealand, as in many other places, these concerns have led to discussions and regulations regarding their use. Key safety concerns include indoor air quality degradation, carbon monoxide poising, NO2 emissions, moisture and mould and more.
Typically speaking it is not advised to use an unflued gas heater to heat your home due to these reasons.
Pros of Unflued Gas Heater
The reason people use unflued gas heaters is because they are highly efficient, converting almost all the gas they consume into heat.
Due to their portability, they can be moved from room to room as needed, providing flexible heating solutions.
Additionally, unflued gas heaters are known for their quick heat-up times, making them ideal for those chilly mornings or evenings.
They also require no installation or structural modifications to the property, making them a less intrusive and more cost-effective option.
Lastly, unflued gas heaters are often praised for their silent operation, providing warmth without the noise disturbance common to other heating systems.
Cons of Unflued Gas Heater
Despite some benefits, unflued gas heaters also come with their own set of drawbacks that are important to consider.
- Indoor air pollution: Unflued gas heaters release combustion products directly into the room, including nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide, potentially causing health problems.
- Ventilation dependence: These heaters rely heavily on sufficient ventilation to avoid build-up of harmful gases. Without it, the risk of exposure increases.
- Condensation issues: The released moisture can lead to condensation and mould growth, damaging property and negatively affecting indoor air quality.
- Efficiency: Unflued heaters are generally less efficient than flued versions. They can consume more gas and lose heat through the required ventilation, increasing operational costs.
Are Gas Fireplaces Flued or Unflued?

Transitioning from heaters to gas fireplaces, it’s important to note that these can also be categorised as flued or unflued, each carrying its own set of advantages and potential drawbacks. Just like heaters, the distinction between flued and unflued gas fireplaces lies in their venting systems.
Flued gas fireplaces are vented to the outdoors, removing combustion by-products from your living space. Unflued fireplaces, on the other hand, expel these by-products into the room they are placed in. Here are the key differentiators between the two:
- Safety: Flued fireplaces are generally considered safer as they eliminate the risk of indoor air contamination. Unflued fireplaces can potentially release harmful gases like carbon monoxide into your home if not properly maintained.
- Efficiency: Unflued fireplaces tend to be more efficient since they utilize the heat produced directly without any loss through a vent.
- Installation: Flued fireplaces require more complex installation due to the need for a chimney or vent, making them typically more expensive to install.
- Maintenance: Unflued fireplaces require more frequent checks and maintenance to ensure safe operation due to the lack of a venting system.
Should You Buy a Flued or Unflued Gas Heater?
Determining whether a flued or unflued gas heater best suits your needs requires careful consideration of several factors, including installation costs, efficiency, safety, and flexibility.
Flued gas heaters, while initially more expensive due to the need for a flue or chimney installation, offer superior safety by directing combustion fumes outside, making them a desirable choice for home heating, especially for families with children or those with respiratory conditions. Additionally, they tend to be more efficient in the long term as they retain more heat, reducing ongoing energy costs.
On the other hand, unflued gas heaters are less expensive to install, and offer greater flexibility as they can be moved to different rooms as needed. However, they pose a higher risk as combustion fumes are released into the room, which can cause health problems if not properly ventilated.
Ultimately, your decision should be guided by your specific needs and circumstances. If safety and efficiency are your primary concerns, a flued gas heater is the optimal choice. However, if cost and flexibility are more important, an unflued gas heater could be a suitable temporary option.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Health Implications of Using Flued or Unflued Gas Heaters?
Flued heaters vent exhaust gases outside, reducing indoor air pollution. In contrast, unflued heaters can cause health issues due to indoor pollutants like nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide, especially in poorly ventilated spaces.
What Are the Installation Costs Associated With Flued and Unflued Gas Heaters?
Flued heaters typically cost more due to the need for vent installation, while unflued heaters are less costly and usually don’t require much installation.
Are There Specific Maintenance Requirements for Flued and Unflued Gas Heaters?
Yes, both types of heaters have specific maintenance requirements. Flued heaters require periodic chimney inspections and cleaning, while unflued heaters need regular checks for potential leaks and proper ventilation for safety reasons.
How Long Is the Typical Lifespan of Flued and Unflued Gas Heaters in New Zealand?
The typical lifespan of gas heaters, both flued and unflued, largely depends on their usage and maintenance. However, on average, well-maintained gas heaters can last between 10 to 20 years.
Looking For a Gas Heater For Your Home?
We supply and installed gas heaters for a wide range of applications including flued, indoor and outdoor. If you are looking to install a gas heater in your home, speak to us today by calling 022 444 6474 or email info@complexplumbing.co.nz.

